Unlike cookies, Session (session) data is stored on the server.The session is the interval at which the client logs on to the server and logs out the server.The data that is required to be saved in the session is stored in a temporary directory on the server.
Assign session IDs to sessions for each client. Session data is stored at the top of the cookie, and the server signs it in encrypted mode.For this encryption, the Flask application requires a defined SECRET_KEY.
Related course: Python Flask: Create Web Apps with Flask
Session
Session object
A Session object is also a dictionary object that contains key value pairs for session variables and associated values.
For example, to set a ‘username’ session variable, use the following statement:
1 | session['username'] = 'admin' |
To release a session variable, use the pop() method.
1 | session.pop('username', None) |
Session example
The following code is a simple demonstration of the session work in Flask.The URL ‘/‘ only prompts the user to log in because the session variable’ username ‘ is not set.
1 |
|
When the user navigses to the “/login” login () view function, because it is invoked through the GET method, a login form opens.
The form is sent back to ‘/login’ and the session variable is now set.The application is redirected to ‘ /‘.The session variable ‘username’ was found at this time.
1 |
|
Run the application and access the home page.(Ensure that the application’s secrett_key is set)
1 | from flask import Flask, session, redirect, url_for, escape, request |
The output is displayed as follows. Click the “Click here” link.
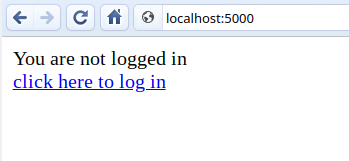
The link will be redirected to another screen. Type “admin” and login. The screen displays the message “Logged in as administrator.”
Related course: Python Flask: Create Web Apps with Flask